Direct Inward Dialing improves customer experience by allowing direct extension dialing.
In this article, we will understand how DID works and its advantages can help businesses improve communication and productivity.
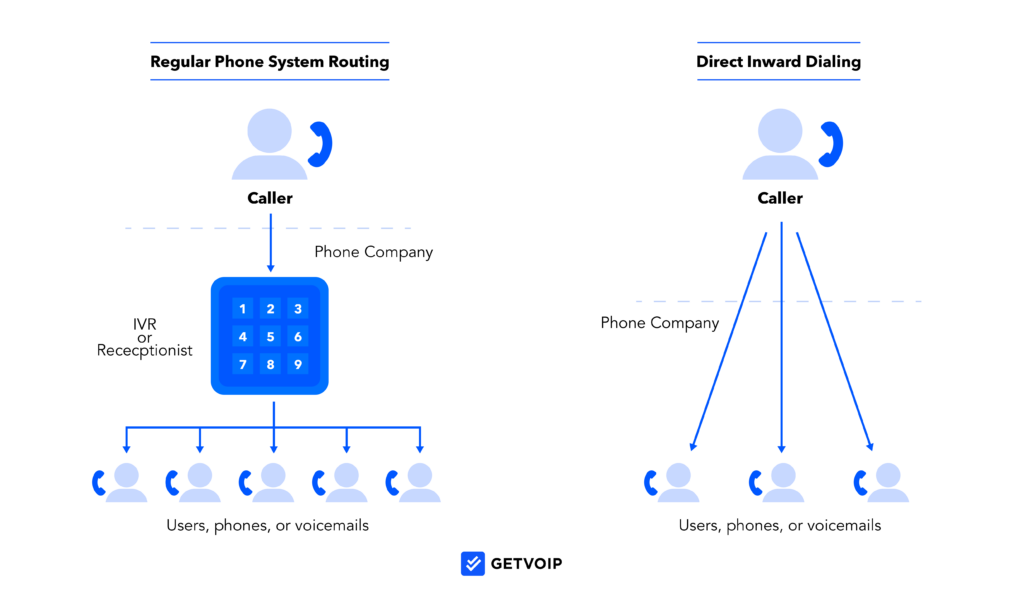
What is Direct Inward Dialing?
- Direct Inward Dialing (DID), also called Direct Dial-In (DDI), is a feature offered by telephone companies that enables external callers to dial directly to an internal extension on a company’s private branch exchange (PBX) phone system.
- DID provides a unique phone number for each employee that can be dialed by customers and other outside callers to connect with them directly, without going through a receptionist or directory service.
- The local phone provider assigns a range of DID numbers to the company for use with their extensions. These DID numbers are linked to corresponding internal extensions.
- When an outside caller dials a DID number, the telephone company routes the call directly to the linked receiving extension at the company’s PBX.
- DID allows for any quantity of simultaneous incoming calls up to the capacity of the PBX phone system.
What is a DID Number?
- A DID number is a Direct Inward Dial phone number assigned by the telephone company to a business for connection to their PBX extensions.
- DID numbers enable outside callers to dial directly to individual employees or departments right on their direct lines, bypassing a switchboard.
- DID numbers are normal-looking 10-digit phone numbers using the standard numbering plan in the region.
- The company can assign each employee their individual DID number that rings to their direct extension.
- DID numbers all point back to the main business PBX but route to the specified direct extension when dialed.
- Companies are allocated a range of DID numbers in sequential blocks of typically 20, 50, or 100 numbers.
How Does Direct Inward Dialing Work?
Direct Inward Dialing works through interaction between the telephone company’s digital telephony switches and the customer’s PBX phone system:
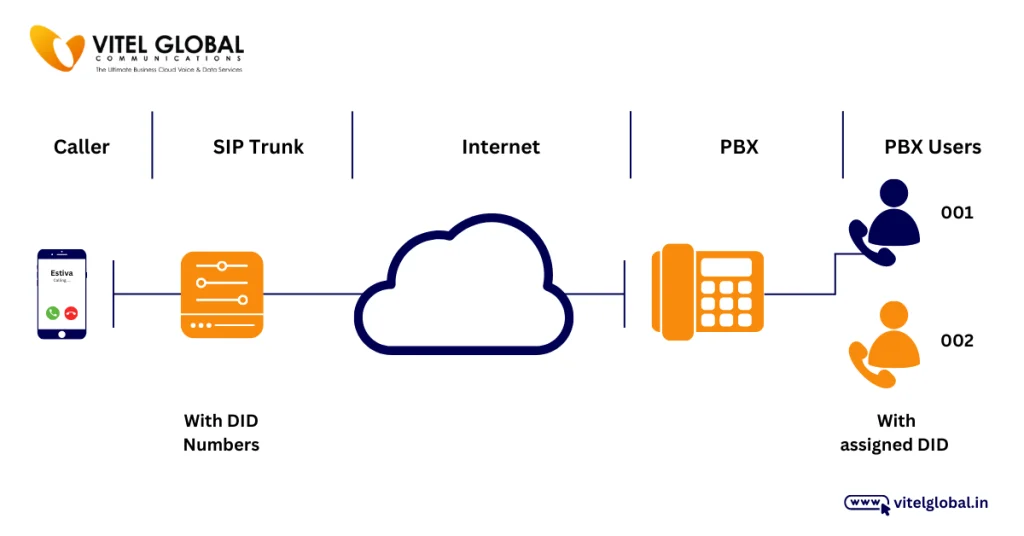
- The local telephone provider allocates a range or block of DID numbers to a business for their exclusive use.
- The business assigns each of these DID numbers to correspond to individual user extensions on the PBX phone system.
- The telephone company programs its digital switches to route inbound calls for each DID number to the PBX trunk lines.
- When an outside caller dials a DID number, the phone company’s switch interprets the number and directs the call to the PBX system.
- The PBX receives the inward call and automatically routes it to the assigned internal extension that corresponds to the DID number being called.
- This enables any quantity of individual DID numbers to ring directly to their matched extensions simultaneously.
- Callers don’t have to memorize extension numbers, improving customer experience.
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) vs Direct Outward Dialing (DOD)
While often confused, DID and DOD are distinct direct dialing functions:
- DID enables external callers to dial inward directly to employees at a company. DOD allows employees to dial outbound calls directly.
- DID routes incoming calls to PBX extensions. DOD allows dialing outside calls without going through a switchboard operator.
- DID provides direct extension numbers for inbound calls. DOD grants direct outgoing external access.
- DID requires programming at the telephone company switch. DOD involves configuration on the PBX phone system.
- Companies use DID to improve inbound customer experience. DOD boosts employee productivity by making outbound calls.
- DID facilitates inbound traffic directly to employees. DOD controls and manages employee outgoing call access.
Benefits of DID
There are many benefits DID inbound calling provides for businesses:
- Improves customer experience allowing direct dialing to employees or departments.
- Increases inbound call capacity with the availability of multiple simultaneous DID numbers.
- Enables individual employee recognition by giving each their number.
- Allows flexible extension assignments as employees join or depart.
- Simplifies contact management for clients with direct dial numbers.
- Avoid the bottleneck of transferring or holding all calls through a receptionist.
- Enables organizations to port existing DID numbers when changing business locations or phone systems.
- Provides a full-featured business phone presence and professional image for small companies.
- Integrates conveniently with automated attendants, voicemail systems, and phone menus.
- Supports detailed tracking of calls to individual DID numbers using call analytics.
How to Get DID?
Follow these steps to get Direct Inward Dialing numbers for your business:
- Determine how many DID numbers you need for existing extensions and potential growth. Common blocks are 20, 50, or 100 numbers.
- Contact your local telephone company to order DID service. The provider will assign your company a range of DID numbers corresponding to your requested block.
- Choose which DID number you want to assign to each extension on your business phone system. Develop a mapping plan.
- Configure your PBX system to route inbound calls from each assigned DID number to its corresponding user extension.
- Confirm with the telephone provider that your DID numbers are programmed in their digital switches to direct inward calls to your PBX trunks.
- Begin distributing DID number assignments to employees and departments.
- Update business materials with individual DID phone numbers for sales, support, departments, and employees.
- Leverage DID call routing to handle growth by adding new user extensions mapped to newly allocated numbers.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What does the acronym DID stand for?
Ans: DID stands for Direct Inward Dialing. It is also sometimes referred to as Direct Dial-In.
Q2: How do DID numbers work on a PBX phone system?
Ans: The business PBX programming routes each inbound DID number to its assigned corresponding internal extension when calls are received.
Q3: What are the advantages of DID numbers for customers?
Ans: DID enables customers to dial employees directly without going through a receptionist or phone directory. This improves customer experience.
Q4: How many DID numbers can a business obtain from their phone provider?
Ans: Telephone companies typically allocate DID numbers in blocks of 20, 50, 100, or more. Companies can request sufficient DID numbers for all their extensions.
Q5: Can existing phone numbers be converted to DID?
Ans: Yes, most providers can convert your current business phone numbers to DID numbers mapped to your PBX extensions. Porting numbers is common when activating DID service.