DECT (Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications) is a standard for short-range wireless communications primarily used for cordless phones, wireless headsets, and other voice applications.
Developed in Europe in the early 1990s, DECT provides low-power, high-quality voice transmission between handsets and base stations using digitally encoded radio signals in the 1.88 to 1.90 GHz frequency band.
With features like security encryption, power control, roaming support, and clear voice quality, DECT has been widely adopted for wireless voice and VoIP.
Over 100 million new DECT systems are sold globally each year for home and enterprise use. Major applications include cordless telephony, wireless PBX extensions, baby monitors, and audio transmitters.
As wireless connectivity demands grow, DECT continues to evolve with higher data rates and expanded capabilities.

DECT Standards and Technology
DECT is based on a common standard defined by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). The primary specifications include:
- Physical layer protocols for radio transmission in the 1880-1900 MHz band
- Methods for multiple access between devices using time division multiplexing
- Support for interoperability, authentication, encryption, power control, and roaming
- Voice codec algorithms for efficient encoding of audio
- Frame and protocol definitions for signaling and messaging
DECT devices operate in the 1880-1900 MHz frequency range, which provides ten radio frequency channels.
Each channel is divided into 24 time slots using TDMA that are allocated dynamically between devices. A DECT base station can support up to 120 simultaneous calls.
DECT uses Gaussian frequency shift keying for robust modulation.

DECT Variants and Capabilities
Several variants of DECT have emerged with additional capabilities:
- DECT GAP – Generic access profile that ensures interoperability between base stations and handsets from different manufacturers.
- DECT 6.0 – Provides improved range, audio quality, and resistance to interference by using more radio channels. Used in many cordless phones.
- DECT ULE – Ultra-low energy version targeting wireless sensors and home automation applications.
- DECT 2020 – Next-generation DECT standard adding capabilities like high-definition voice, audio conferencing, wideband data, and low latency.
- CAT-iq – Version of DECT developed by the DECT Forum to support wireless VoIP and advanced enterprise applications.
Applications and Uses of DECT
DECT technology has many applications and use cases:
1. Cordless Telephony
DECT is widely used for cordless phones and wireless handsets working with a base station connected to a landline. Provides private, secure calls with a good range from the base.

2. Wireless PBX/VoIP
In business settings, DECT is used to connect cordless headsets and handsets to an IP-PBX or VoIP phone system to enable mobile voice access.
3. Baby Monitors
Baby monitors use DECT to stream audio between the child unit and the parent unit up to 300 feet apart, allowing remote monitoring of babies.
4. Wireless Headsets
DECT supports quality wireless audio for applications like Bluetooth headsets for phone calls, gaming headsets, and headphones for TV or music listening.
5. Home Wireless Audio
Wireless DECT audio transmitters can stream stereo audio from a music source to speakers in multiple rooms without wiring.
6. Wireless Sensors
DECT ULE allows for interoperable connected home sensors for smart home automation, with multi-year battery life for sensors.
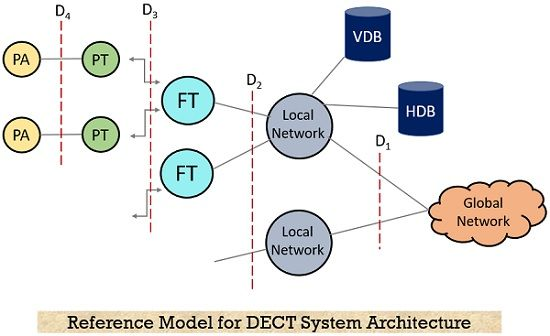
Benefits of DECT
DECT offers numerous benefits:
- Proven technology – Widely deployed and adopted wireless standards for over 25 years.
- Global interoperability – Devices from different manufacturers work together seamlessly.
- Voice quality – Provides clear voice quality with robust anti-interference capabilities.
- Range – Allows flexibility with cordless operation up to 500 feet from the base.
- Security – DECT standards include strong authentication and voice encryption.
- Low latency – Optimized for real-time voice and audio streaming applications.
- Low power – Long battery life measured in months/years for many devices.
- Scalability – A single base can support over 100 handsets for large deployments.
Challenges for DECT
Some key challenges exist with DECT technology:
- Limited bandwidth and data rates – DECT is designed for voice and low bandwidth applications, not high-speed data.
- Interference concerns – Only 10 radio channels, so interference is possible in dense deployments.
- Limited non-voice applications – Few uses for DECT other than cordless voice communications.
- Complexity – Advanced DECT capabilities require some complexity in base stations.
- Proprietary implementations – Some vendors implement non-standard versions of DECT.
- Deployment costs – DECT systems require compatible handsets and base station infrastructure.
Future of DECT
DECT is likely to remain a key technology for cordless voice and audio applications with some potential future developments:
- Higher bandwidth variants to support applications like multimedia streaming.
- Expanded usage in wireless sensors and IoT devices.
- Seamless integration with VoIP and IP phone systems.
- Support for cellular integration and Wi-Fi roaming.
- Adoption in enterprise settings for mobility applications.
- Next-generation DECT advancing capabilities for professional and consumer devices.
Even with the rise of VoIP and cellular, DECT fills an important role for short-range wireless voice and audio that is likely to continue.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Ques 1. What is the range of DECT devices?
Ans. DECT devices typically have a range of up to 500 feet outdoors and 150 feet indoors from the base station. The range depends on interference, obstacles, and implementation.
Ques 2. How secure is DECT?
Ans. DECT uses authentication and over-the-air voice encryption to provide secure communications resistant to eavesdropping. However, early versions had some vulnerabilities.
Ques 3. Can DECT support Wi-Fi or mobile connectivity?
Ans. Some newer DECT systems allow dual-mode support for cellular or Wi-Fi alongside DECT. This allows routing calls and data over DECT or other networks.
Ques 4. What frequency bands are used by DECT globally?
Ans. The core DECT frequency range is 1880-1900 MHz. But in the Americas, DECT operates between 1920-1930 MHz. Global roaming requires supporting multiple bands.
Ques 5. Is DECT used outside of Europe?
Ans. Yes, DECT has been widely adopted worldwide, especially for cordless phones. Over 600 million DECT systems have been sold globally to date. Major markets include Europe, the US, and Asia.






