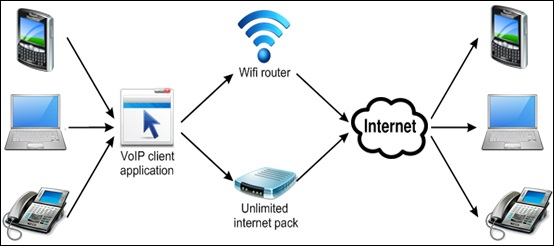
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a technology that allows people to make phone calls over the Internet instead of traditional phone lines.
VoIP converts your voice into digital signals that travel over the internet, then converts it back into sound on the other end so you can speak to someone.
The benefits of VoIP include lower costs, more features, and greater flexibility compared to old landline phones.
This detailed guide will explain everything you need to know about VoIP technology.
It covers what VoIP is, how it works, the difference between VoIP, SIP, and PBX systems, the pros and cons of VoIP, how much it costs, the equipment you need, and what to look for in a VoIP provider.
Even if you’re new to VoIP, this extensive article makes the technology easy to understand from top to bottom.

How Does VoIP Work?
VoIP converts analog voice signals into digital data packets using a codec (coder/decoder). Common codecs include G.711, G.729, and G.722.
These digitized packets are compressed and sent over the internet using your broadband connection.
Packets are then received by the other party’s VoIP phone, decompressed, converted back into an analog audio signal, and played through their phone. This all happens very rapidly.
VoIP protocols like Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and H.323 are used to establish, route, and terminate VoIP calls.
To place a call, your VoIP phone sends a request to connect to the VoIP provider’s servers. It is authenticated then a connection is made between you and the person you are calling.
The technical process behind a VoIP call includes:
- Analog to digital conversion – Voice signals are converted into digital packets by a codec.
- Compression – Packets are compressed to optimize bandwidth usage during transmission.
- Packetization – The compressed data is organized into packets and assigned header information for routing.
- Transmission – Packets travel over the internet using protocols like SIP, RTP, UDP, and TCP.
- Decompression – Packets are decompressed by the receiving codec.
- Conversion – The digital data is converted back into analog signals.
- Playback – The analog signals reach the recipient’s phone and are played as normal sound.
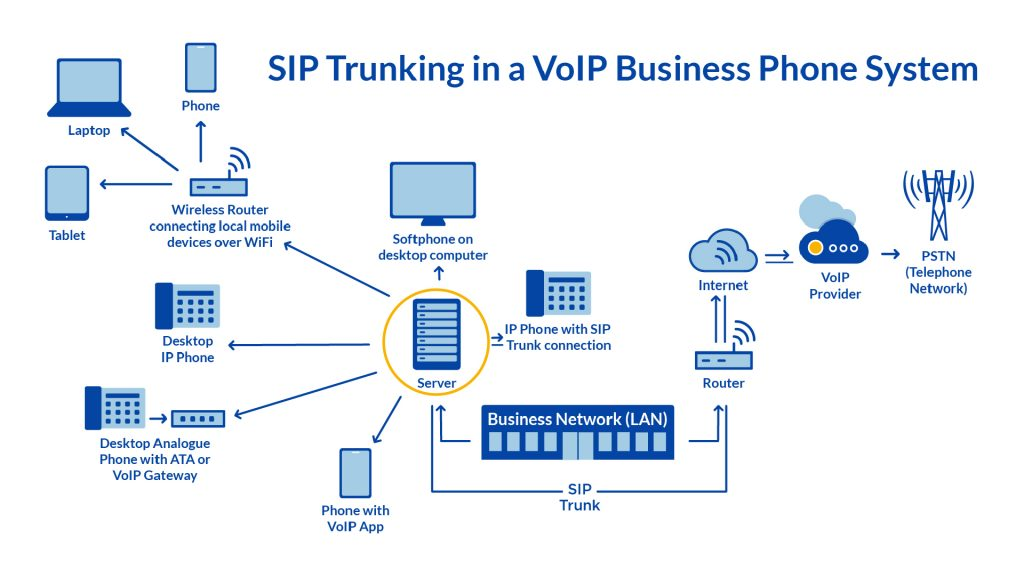
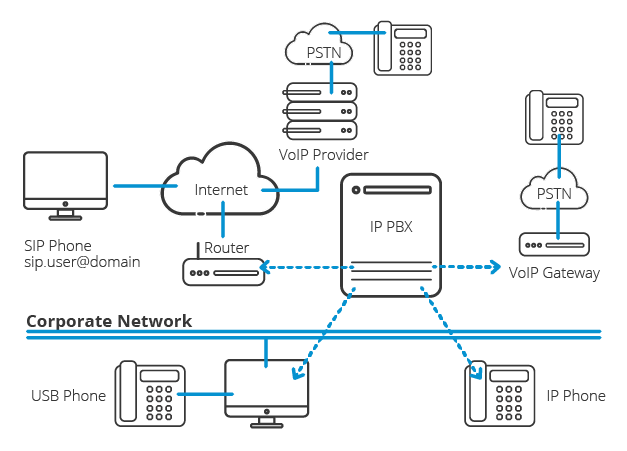
VoIP vs SIP vs PBX
1. VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol)
It allows making phone calls over any broadband internet connection instead of analog phone lines.
This makes it convenient and cost-effective, eliminating the need for traditional expensive phone services.
- VoIP converts voice into packets of digital data and transports it over IP networks. This allows the integration of voice and data networks.
- VoIP utilizes codecs to compress and convert voice streams into IP packets and back to audible voice format at the receiving end. Common codecs used are G.711, G.729, G.722.
- VoIP protocols like SIP, RTP, and SDP are used to set up, manage, and terminate VoIP calls.
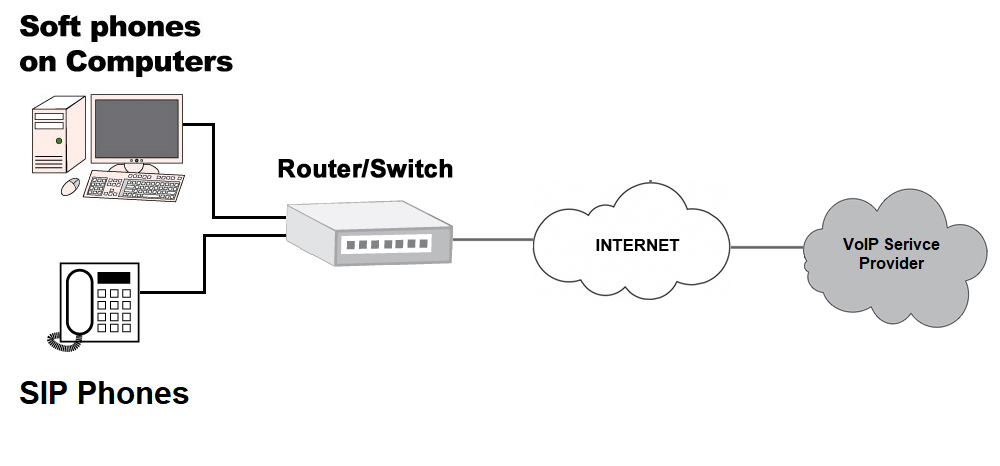
2. SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
It is a signaling protocol used for controlling communication sessions like voice and video calls over IP networks. SIP handles the setup and teardown of VoIP calls.
- SIP establishes, manages, and terminates multimedia sessions including VoIP calls by sending requests between endpoints.
- It handles addressing and routing functions enabling endpoints to locate and connect to other endpoints.
- SIP works in conjunction with other protocols like SDP, RTP, T.38, etc. to facilitate media transfer between endpoints once the call is set up.
3. PBX (Private Branch Exchange)
It is a private telephone network used by businesses to manage multiple internal phone lines and route calls. Key aspects:
- PBX provides a company with an internal phone system allowing shared access to a certain number of external phone lines.
- It enables employees to make internal calls between extensions and provides external call routing from a company’s phone network.
- Features include call forwarding, call transfer, voicemail, teleconferencing, auto attendants, etc.
- PBX offers central control over the phone system managed through PBX software. It provides analytics of call traffic, call distribution, management of extensions, etc.
- PBX can integrate with analog, digital, or VoIP phone systems. IP-PBX supports VoIP phones and PBX features over corporate IP networks.
Overall, VoIP is the technology to make voice calls over IP. SIP is a key VoIP signaling protocol for session management.
PBX offers a centralized business phone system, while VoIP-based IP-PBX integrates it with VoIP and IP networks.
Key VoIP Provider Features
1. Top business VoIP providers offer:
- 99.99% or higher uptime SLA
- Free calling between users and offices
- Unlimited minutes options
- Mobility features to use your business number on mobile
- Auto attendants and call routing
- Visual dashboards and call analytics
- CRM and helpdesk integrations
- Toll-free numbers and vanity numbers
- Scalable seats and extensions
- Integrated faxing and conferencing
2. VoIP Call Quality Considerations
To ensure good call quality, your business should have:
- High-speed wired internet with at least 10-25+ Mbps
- Low latency and jitter – should be under 150ms for optimal quality
- QoS configurations on your router to prioritize voice traffic
- Proper routers, switches, and ethernet cabling
- VoIP phones connected directly to the router via ethernet
With a fast, reliable wired network, modern VoIP services sound as good as traditional phones. Call quality issues are uncommon on properly configured systems.
3. Transitioning to VoIP
Switching your business phones to VoIP requires:
- Choosing a reliable VoIP provider and plan
- Ordering new VoIP phones and equipment
- Installing phones, cables, switches, and routers if needed
- Configuring your VoIP system and porting over numbers
- Testing call quality and features
- Training staff on using the new VoIP system
- Retiring old analog and digital phone hardware
A qualified VoIP technician can handle the implementation and ensure a smooth transition.
Pros and Cons of VoIP
Pros:
- Cost savings – VoIP is much cheaper than traditional landline phones and can save businesses 30-70% on phone bills.
- Advanced features – Get sophisticated features with VoIP that regular phones lack, like auto attendants, web interfaces, call analytics, and more.
- Flexibility – VoIP works from anywhere with an internet connection. Users can take their VoIP phone number with them anywhere.
- Scalability – VoIP systems can be scaled up or down easily as your business grows or shrinks.
- Reliability – VoIP providers implement redundancy so phone service is not impacted by internet outages. Call quality is very reliable on fast, modern networks.
Cons:
- Sound quality issues can occur on very slow internet connections, resulting in lag, jitter, static, or garbled call quality. This is rare on wired networks.
- You are dependent on your internet connection. If your business’ internet goes down, your phones go down too.
- Switching providers isn’t as easy. You may need to get new phones or adapters.
- Power outages cause phones to stop working unless you have a backup power source.
How Much Does VoIP Cost?
VoIP is generally much cheaper than traditional wired phone service. Here are some typical VoIP pricing options:
- Residential VoIP plans cost $20-$30 per month on average, sometimes as low as $10 per month.
- Small business VoIP with a handful of phones usually costs between $20-$40 per user per month. Comes with more features.
- Larger enterprise-level systems for big companies are $25-$50 per user monthly.
- Pay-by-minute plans are about 2-3 cents per minute.
- Unlimited calling plans are $30-$50 per user monthly. Popular for call centers and offices.
- International calling can be included very cheaply or sometimes for free.
Many providers let you customize your features and minutes, so your monthly cost will depend on your needs.
Essential Equipment and Hardware
To use VoIP, you’ll need:
- VoIP telephone – Options include dedicated VoIP desk phones, VoIP-enabled mobile apps, and VoIP adapters to connect regular phones to the internet.
- Router – A modern, high-quality business router with QoS settings enabled. This helps prioritize voice traffic.
- Ethernet cabling – VoIP phones need to connect directly to your router via ethernet for the best call quality.
- Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) – A UPS provides backup power in case of electricity loss. This prevents phones from going dead during an outage.
Optional extras can include headsets, wireless networking hardware for mobile phones, phone switches, and tools for setting up phone numbers and extensions.
Choosing VoIP Phones and Equipment
When selecting VoIP phones and hardware, consider these factors:
- Wired vs wireless – Wired VoIP phones typically provide better call quality than wireless. But wireless VoIP phones offer more flexibility.
- Power over Ethernet – PoE VoIP phones don’t require a power outlet and can operate simply over your ethernet cable. Very convenient.
- Expandability – Many VoIP phones and PBX systems allow you to easily add extensions, phone lines, and handsets as your team grows.
- Call management features – For large businesses, opt for equipment with advanced call routing, auto attendants, ring groups, and reporting.
- Phone type – Choose from basic VoIP phones, executive phones with additional features, conference phones, and mobile VoIP apps.
- Budget – VoIP equipment ranges from basic $50 models to advanced $300+ enterprise-grade phones with more capabilities.
- Vendor – Stick with major brands like Polycom, Cisco, Yealink, and Grandstream for reliable hardware.
What to Look For in a VoIP Provider?
When comparing business VoIP providers, look for these features:
- Strong uptime record – Ask about the provider’s service availability levels to make sure reliable call quality is a priority.
- Quality phone plans – Look for unlimited nationwide calling, unlimited long-distance, and cheap international rates.
- Scalability options – Can the provider easily scale up or down as your users and needs change?
- Tech support – Pick a provider with 24/7 customer and technical support in case you ever have issues.
- Security features – Encryption, user authentication protocols, and other security measures to protect your systems.
- Calling features – Useful calling tools like auto-receptionist, call forwarding, conferencing, reporting, and call queues or IVR.
- Reviews – Check credible online reviews to ensure high call quality and customer satisfaction.
- Prices – Compare the pricing of features, minutes, and additional phones or extensions to get the best deal.
Conclusion
VoIP solutions provide tremendous value, features, and flexibility compared to traditional business phone systems.
With VoIP, businesses can reduce costs, streamline communications, and enable remote work.
This guide covered everything you need to know, from the technology behind VoIP to features, benefits, costs, equipment, providers, and more.
The detailed information here empowers you to make smart decisions as you transition to next-generation cloud phone service for your business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Ques 1. How reliable is VoIP?
Ans. VoIP call reliability is excellent on modern networks. Top providers guarantee 99.99% uptime. Quality issues are very rare on fast-wired connections.
Ques 2. Does VoIP work with power outages?
Ans. VoIP phones will not work during power outages unless you have a backup power source like a UPS. Analog lines work if the telephone company has backup power.
Ques 3. Is VoIP secure?
Ans. VoIP encryption and authentication protocols provide good security. Transmissions are all digital making them difficult to tap. Proper cyber security is still important.
Ques 4. What internet speed do I need?
Ans. VoIP needs at least 10-25 Mbps internet speeds for optimal call clarity. Even faster is better, especially for multiple concurrent calls.
Ques 5. Can I make emergency calls?
Ans. Yes, but you must register your VoIP phone address so 911 dispatchers know your location. Mobile networks are better for emergency calls.